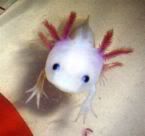

SCIENTIFIC CLASSIFICATION
COMMON NAME: axolotl, Mexican axolotl, Mexican salamander, Mexican walking fish
KINGDOM: Animalia
PHYLUM: Chordata
CLASS: Amphibia
ORDER: Caudata
FAMILY: Ambystomatidae [salamanders]
GENUS SPECIES: Ambystoma mexicanum
FAST FACTS
DESCRIPTION:
Axolotls may exhibit a variety of colors, including gray, tan, brown, white, golden albino, white albino, and blue
SIZE: 20-30 cm (10-12 in.)
WEIGHT: Up to 300 g (8 oz.)
DIET: Small aquatic creatures including worms, insects, crustaceans, and small fishes
INCUBATION: 2-3 weeks
CLUTCH SIZE 200-1,000+ eggs in a single spawning
SEXUAL MATURITY: 6-12 months
LIFE SPAN: Axolotls may live more than 10 years
RANGE: Native to both Lake Xochimilco and Lake Chalco (no longer in existance) of Mexico
HABITAT: Freshwater lakes, usually murky
POPULATION: GLOBAL No data
STATUS: IUCN Vulnerable
CITES Appendix II
USFWS Not listed
FUN FACTS
1. One derivation of the name 'axolotl' references the Aztec god Xolotl, the god of games who could turn himself into an axolotl to escape his enemies.
2. An axolotl's skeleton is comprised mostly of cartilage. They exhibit neoteny, meaning they retain juvenile characteristics into adulthood.
3. They are aquatic, and although they posses rudimentary lungs, they breathe primarily through their gills and, to a lesser extent, their skin.
4. If axolotls spend prolonged periods of time in shallow water, their gills may be absorbed and they can begin using their lungs on land. However, if axolotls are in deep water for long, they will keep their gills for the remainder of their lives, or until they move to shallow water for a long period of time.
5. Axolotls have amazing healing abilities. Normal wound healing in animals occurs through the growth of scar tissue, and this means that most animals won't re-grow a lost limb. However, the axolotl is fully capable of complete limb re-growth.
ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION
Amphibians have porous skin and respond quickly to changes in the environment-the health of their populations can be an indicator of the health of the environment. Axolotls are important in medical and scientific research because of their unique regenerative qualities as well as their neotenic characteristics.
MANTELLA FROGS


SCIENTIFIC CLASSIFICATION
COMMON NAME: Mantella frog, living jewel
KINGDOM: Animalia
PHYLUM: Chordata
CLASS: Amphibia
ORDER: Anura
FAMILY: Mantellidae
GENUS SPECIES: Mantella spp. (16 species)
FAST FACTS
DESCRIPTION:
Mantella frogs are tiny tree frogs and occur in color combinations of dark black and iridescent blues, oranges, yellows, and greens.
SIZE: Up to 5 cm (2 in.)
WEIGHT: Up to 56 g (2 oz.)
DIET: Diurnal predators, these frogs prey mainly on insects and often prey upon ants and termites
INCUBATION: The egg-laying site is normally a moist and enclosed location like depressions in sponge or moss. Several males fertilize eggs either immediately following deposition or up to 2 days after. Incubation is 2-6 days.
CLUTCH SIZE The number of eggs laid varies with species and maturity of the female.
LARVAL DURATION Tadpoles metamorphose after 45-360 days, depending on the species.
SEXUAL MATURITY: 12-15 months
LIFE SPAN: 5-10 years
RANGE: Madagascar
HABITAT: Ground-dwellers living in the forests
POPULATION: GLOBAL No data
STATUS: IUCN Not listed
CITES Appendix II
USFWS Not listed
FUN FACTS
1. Mantella frogs are among the most brightly colored and showy of all frogs. These colors may act as a warning to predators, which is termed aposomatic coloration.
2. Most Mantellas have the same toxins found in the South American poison dart frogs. In fact, when explorers first saw mantella frogs they thought they were South American poison dart frogs, but they are only distant relatives.
3. Several species of Mantella frogs are non-poisonous, but exhibit protective mimicry. By exhibiting the bright colors of the toxic species, they are avoided by predators.
4. Since they often prey on ants and termites, mantella frogs are diurnal.
5. In general, frogs have smooth skin while toads have textured skin.
6. A group of frogs is called an 'army'; a group of toads is called a 'knot'.
7. Frogs with long tongues go by the "see it, snap at it" technique of feeding. Toads on the other hand have short tongues and have to snap at their food using their mouth.
8. When a frog swallows a meal, its bulgy eyeballs close and sink in to its head. The eyeballs apply pressure and actually push a frog's meal down its throat.
ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION
Like all amphibians, Mantella frogs have porous skin and respond quickly to changes in the environment. The health of their populations can be an indicator of the health of the environment.
Major threats include: habitat loss, resource exploitation, environmental contaminants, disease and parasitism, introduced species, and global climate change.
11 of the species are classified either commercially threatened, rare, or vulnerable. Only 1 species is not considered threatened. Some species are endemic to very small areas, making them sensitive to over-collection.







0 comments:
Post a Comment